
A pulley is a simple type of machine consisting of a wheel with a slot around its perimeter that allows a rope or cable to be passed through it. Its basic design allows for changing the direction and force needed to lift heavy objects.
The rope that passes through the pulley slot is called a hoist cable and can be powered by a person or a mechanical power source, such as a motor.
How does a pulley work?
A pulley is a simple mechanical device that facilitates lifting heavy objects by changing the direction of the applied force. It consists of a wheel with a groove through which a rope, chain or cable passes.
By pulling on the rope, the pulley causes the force to be directed upward or in another direction, allowing loads to be lifted or moved more easily. In a fixed pulley, the amount of force needed is the same as the weight of the object, but in a movable pulley, the force is reduced by being distributed among several segments of rope.
When multiple pulleys are used in a compound system, such as a hoist, the mechanical advantage is increased, meaning less force needs to be applied to lift heavier objects.
These systems allow much larger loads to be lifted without having to use a force proportional to the weight of the object, taking advantage of the combination of fixed and mobile pulleys.
Advantages and benefits
The main advantage of the pulley is its ability to reduce the amount of force needed to lift a heavy object. This is because it distributes the load across several ropes or cables that support the weight.
If we consider a fixed pulley, where a rope is passed over it and held at both ends, the force applied to lift the object is halved. This is because the weight of the object is equally divided between the rope held and the rope pulled.
Therefore, if a load of 100 kilograms needs to be lifted, only 50 kilograms of force would be required to accomplish this.
The pulley is also very useful for changing the direction of a force. If a load needs to be moved in a direction opposite to that in which the force is applied, a pulley can be used. By passing the lifting rope through the pulley and then applying the force in the opposite direction, the desired displacement is achieved. This is especially useful in situations where space is limited or when obstacles need to be avoided along the way.
Pulley applications are diverse and can be found in many areas of everyday life and industry. They are used in cranes, elevators, pulley systems in gyms, water lifting systems in wells, among others.
Types of pulleys
In addition to the fixed pulley, there are other types of pulleys that further increase the efficiency of the system. Below are some of the most common types of pulleys:
-
Fixed pulley: This is the most basic type of pulley and consists of a wheel with a groove around its perimeter. The lifting rope or cable is passed over the pulley and is secured at both ends. The fixed pulley only changes the direction of the applied force, but does not provide any additional mechanical advantage.
-
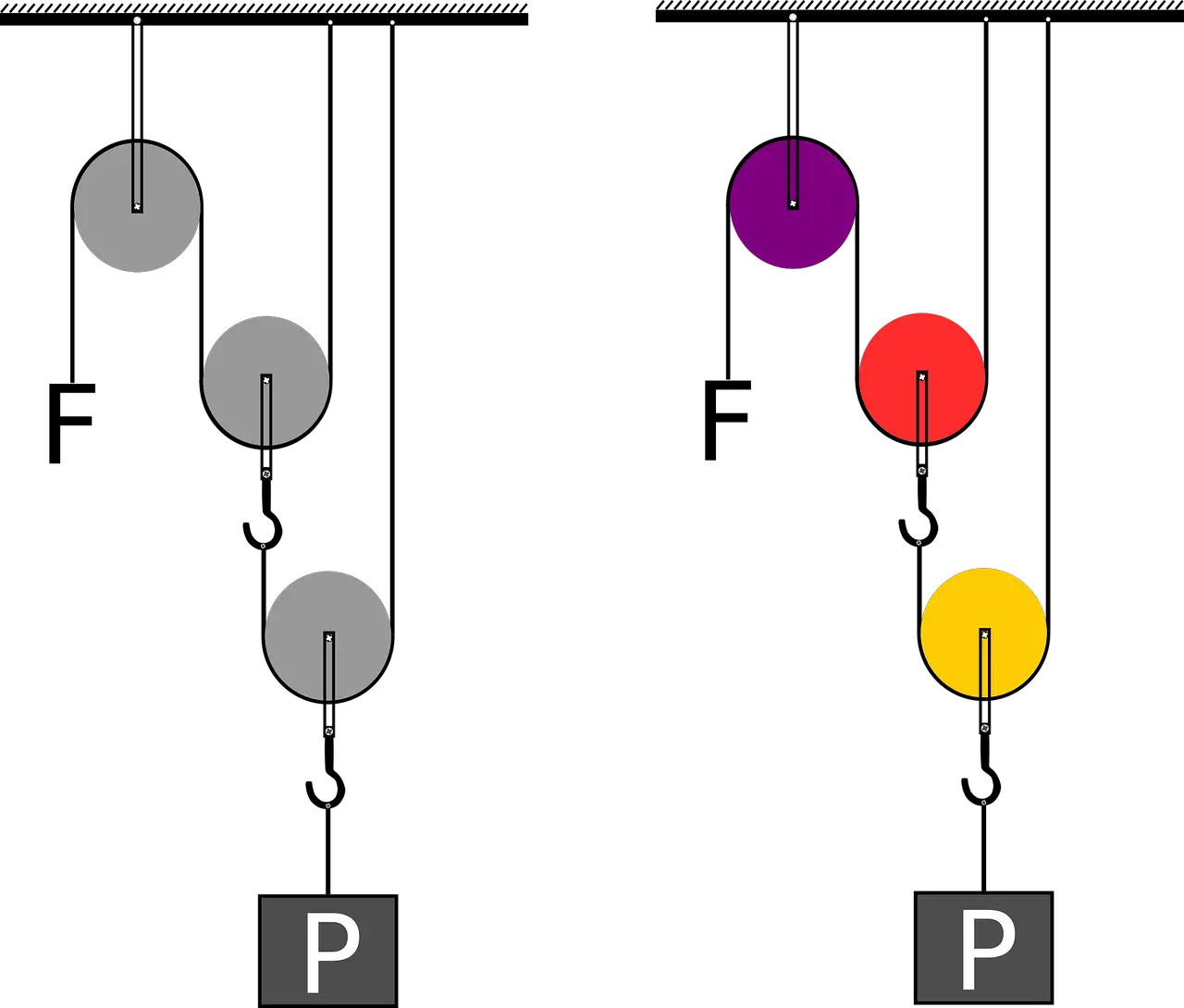 Travelling pulley: Also known as a compound pulley, this consists of a combination of a fixed pulley and a movable pulley. The movable pulley can be moved along the lifting rope and is used to apply additional force to the system. This provides a mechanical advantage, meaning less force is required to lift a given load.
Travelling pulley: Also known as a compound pulley, this consists of a combination of a fixed pulley and a movable pulley. The movable pulley can be moved along the lifting rope and is used to apply additional force to the system. This provides a mechanical advantage, meaning less force is required to lift a given load. -
Tensioner Pulley: This type of pulley is used to maintain proper tension on a belt or chain. It is commonly used in power transmission systems, such as in engines and industrial machinery, to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
-
Reversing Pulley: Also known as a diverter pulley, this is used to change the direction of a rope or cable without applying any mechanical advantage. These pulleys are often used in multiple pulley systems and in applications where a rope needs to be redirected through an angle.
-
V-belt pulley: This type of pulley is used in belt drive systems, where a V-belt is placed around the groove of the pulley. The belt transmits power from one pulley to another, allowing for efficient power transmission in machinery and vehicles.
-
Gear pulley: Instead of having a groove around their perimeter, gear pulleys have teeth that engage with the teeth of another gear pulley. These pulleys are used in power transmission systems where a specific speed ratio and precise transfer of motion are required.
Examples of pulleys
Below are some examples of how pulleys are used in everyday life and in different industries:
-
Elevators: Elevators use pulleys to raise and lower cabins. A pulley system is responsible for supporting and moving the load safely and efficiently.
-
Cranes: Cranes use these simple machines to lift heavy objects in construction, the maritime industry, and other fields.
-
Gyms: Many gym workout equipment, such as cable machines, use pulleys to provide resistance and facilitate controlled movement during exercises.
-
Water wells: In areas where the water supply depends on wells, these devices are used to raise buckets filled with water using a rope. This allows water to be extracted more easily and efficiently.
-
Curtains: Some curtain systems use pulleys to facilitate opening and closing of curtains using a cord. These help reduce the force required to manipulate heavy curtains.
-
Boat sails: On traditional boats, pulleys are used to adjust and control the sails. They also allow the direction and tension of the sails to be changed depending on wind conditions.
-
Escalators: Escalators use pulleys to move steps continuously, allowing people to move from one level to another in places such as shopping malls, airports and train stations.
-
Lawn Mowers: Some models of lawn mowers use pulleys to transmit power from the engine to the blades.