Electrical energy is an essential component of our everyday lives. From lighting our homes to powering our electronic devices and keeping most modern technologies running, this form of energy has revolutionized the way we live and work.
The discovery and understanding of electricity and its ability to do work has been fundamental in the evolution of technology and the improvement of the quality of life.
Definition: What is electrical energy?
Electrical energy is the form of energy generated by the movement of electrical charges, mainly electrons, through a conductor. This energy can be transformed into various useful forms, such as light, thermal or mechanical energy.
It is measured in units such as joules (J) or kilowatt-hours (kWh), and its generation typically occurs in power plants through the conversion of other forms of energy, such as chemical, nuclear, solar, or wind energy.
Electricity is distributed through power grids for use in homes, industries and businesses. It is essential for its ability to be easily transported and its efficiency in conversion to other forms of energy.
Characteristics of electrical energy
 Electrical energy is a form of energy that is distinguished by its unique technical and physical characteristics, making it essential for numerous applications in our daily lives and in industry.
Electrical energy is a form of energy that is distinguished by its unique technical and physical characteristics, making it essential for numerous applications in our daily lives and in industry.
Electrical charge: Electrical energy is directly related to the charge of subatomic particles, mainly electrons and protons. Electrons, with a negative charge, and protons, with a positive charge, are responsible for the generation and propagation of electricity in conductive materials.
Electric current: Electric current is the flow of electric charges through a conductor, and is measured in amperes (A). Although conventional current is defined as the movement of positive charges, in practice it is the negatively charged electrons that move, moving in the opposite direction to conventional current.
Voltage: Voltage, expressed in volts (V), is the difference in electrical potential between two points in a circuit. This potential difference is what drives the flow of electrons and is therefore essential to the generation of electric current. The higher the voltage, the greater the ability to cause current to flow through a conductor.
Resistance: Electrical resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), is the resistance offered by a material to the passage of current. Conductors with high resistance allow less current to pass for the same voltage, which can generate heat as a byproduct.
Electrical Power: Electrical power, measured in watts (W), represents the rate at which work is done using electric current. It is calculated as the product of current and voltage (P = IV). This concept is crucial to understanding the energy consumption of electrical devices and their efficiency.
Energy and Work: Electrical energy, measured in joules (J) or kilowatt-hours (kWh) for more practical applications, is the amount of work that can be done by an electrical system. This energy can be stored, as in batteries, or used immediately to perform various tasks.
Electric field: Electric charges generate electric fields, which are regions of space where other charges experience forces. This concept is fundamental to understanding phenomena such as electromagnetic induction, which enables the generation of electricity in alternators and transformers.
Energy transformation: Electrical energy is extremely versatile and can be converted into other forms of energy, such as mechanical energy in electric motors, light energy in light bulbs, or thermal energy in electric heaters. This transformation capacity is what makes electricity indispensable in a wide range of applications, from the home to industry.
Types of electrical energy
From the point of view of physics, the types of electrical energy can be understood as follows:
Dynamic electrical energy
Dynamic electrical energy is the most common type and relates to moving electric current. It is generated when electrons flow through a conductor, such as a wire, due to an electrical potential difference.
This current can do work, such as lighting light bulbs, running electric motors, or charging electronic devices. There are two types of current: direct current, in which electrons flow in a linear fashion, and alternating current, in which electrons vibrate to generate electrical impulses.
Static electrical energy
 Static electrical energy refers to the accumulation of electrical charges on an object, without any current flow.
Static electrical energy refers to the accumulation of electrical charges on an object, without any current flow.
This occurs when two oppositely charged objects are charged by friction, such as rubbing a balloon on a sweater. Although not used to operate devices, static energy can cause noticeable effects, such as sparks and electrical discharges.
This type of energy is what lightning generates.
Electromagnetic energy
Electromagnetic energy is a form of energy that travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as visible light, microwaves, and radio waves.
These waves consist of electric and magnetic fields that propagate through space, and are fundamental in modern technology, as they allow the transmission of information and the generation of energy through solar panels and antennas.
How is electricity generated?
Electrical energy does not exist freely and in a usable form in nature in forms that can be directly used by humanity. Although we can observe its manifestation in natural phenomena such as thunderstorms, the immense amount of energy generated in these events cannot be captured, stored or controlled in a practical way with current technology.
To meet our energy needs, power plants are responsible for producing electricity from a variety of sources. These sources can be classified into two broad categories: renewable and non-renewable energy sources, depending on their ability to regenerate and the impact their use has on the environment.
Renewable energy sources
 Renewable energy sources are those that are obtained from inexhaustible natural resources or that are naturally regenerated in a short period of time. These forms of energy are not only more sustainable, but they also have a lower environmental impact by not emitting large amounts of greenhouse gases. Some prominent examples of renewable energy include:
Renewable energy sources are those that are obtained from inexhaustible natural resources or that are naturally regenerated in a short period of time. These forms of energy are not only more sustainable, but they also have a lower environmental impact by not emitting large amounts of greenhouse gases. Some prominent examples of renewable energy include:
- Photovoltaic solar energy : This form of energy harnesses solar radiation through photovoltaic panels that convert sunlight directly into electricity. It is a clean and abundant source of energy, especially in regions with high solar exposure.
- Wind energy : It is generated by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy, and then into electricity. Wind farms, both on land and offshore, are key facilities for harnessing this energy source.
- Hydroelectric power : Hydroelectric power plants use the potential energy of water stored in reservoirs or fast-flowing rivers. Through a system of turbines, they transform this energy into electricity. It is one of the most mature and widespread sources of renewable energy in the world.
- Geothermal energy : Harnesses the heat from the Earth's interior to generate electricity. Geothermal power plants extract steam or hot water from underground, which enables turbines to be powered to generate electricity. It is a constant and reliable source in regions with high geothermal activity.
- Biomass : Biomass energy is generated from organic matter, such as wood waste, crops, agricultural residues, and manure. When this matter is burned or processed, thermal energy is produced that can be used to generate electricity. It is a renewable source, since biomass can be regenerated through the natural growth cycle of plants. In addition, when managed sustainably, biomass can contribute to the reduction of net carbon emissions.
- Tidal energy : This energy is obtained by taking advantage of the tides, that is, the rise and fall of the sea level caused by the gravitational attraction of the Moon and the Sun. Tidal power plants use turbines that are moved by the ebb and flow of water, generating electricity. Although their implementation is limited to coastal areas with large tidal differences, they represent a renewable and predictable source of energy.
- Wave energy : Similar to tidal energy, wave energy harnesses the motion of waves on the ocean surface to generate electricity. This type of energy is still emerging, but has great potential due to the vast expanse of the oceans.
Non-renewable energy sources
 On the other hand, non-renewable energy sources rely on resources that exist in limited quantities and are not regenerated on a human time scale. Intensive use of these sources not only contributes to resource depletion, but also generates significant environmental impacts, such as the emission of greenhouse gases. Some examples include:
On the other hand, non-renewable energy sources rely on resources that exist in limited quantities and are not regenerated on a human time scale. Intensive use of these sources not only contributes to resource depletion, but also generates significant environmental impacts, such as the emission of greenhouse gases. Some examples include:
- Nuclear energy : It is obtained from the fission of uranium isotopes, a mineral that, although abundant, is not regenerated. Nuclear power plants generate large amounts of electricity with low direct CO2 emissions, but the management of radioactive waste and the associated risks are major challenges.
- Fossil fuels : These include coal, oil and natural gas, which are organic resources accumulated over millions of years. Thermal power plants that use these fuels generate electricity through combustion, which releases thermal energy. However, their exploitation and use are unsustainable in the long term due to the finiteness of resources and their high impact on climate change.
Transportation and distribution of electrical energy
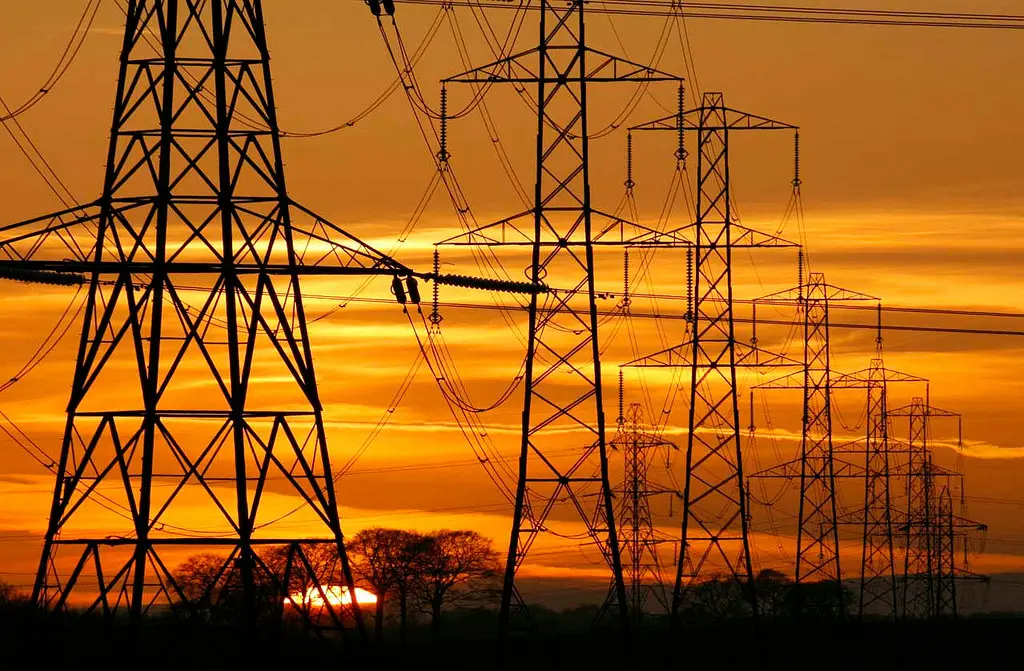 Electric power transmission is a crucial process for delivering electricity from generating plants to points of consumption, such as homes and industries. It begins with the generation of electricity in power plants, which use various sources, such as fossil fuels, hydroelectric, solar or wind energy, to produce electricity using electric generators.
Electric power transmission is a crucial process for delivering electricity from generating plants to points of consumption, such as homes and industries. It begins with the generation of electricity in power plants, which use various sources, such as fossil fuels, hydroelectric, solar or wind energy, to produce electricity using electric generators.
Once generated, electricity is transported over long distances via high-voltage transmission lines. These lines minimise energy losses during transport and can operate on alternating or direct current depending on the needs. At transmission substations, the voltage is adjusted and different energy sources are interconnected.
The electricity is then distributed through local distribution networks, using lower voltage, alternating current lines. Transformers are used to adjust voltage levels throughout the process. Distribution substations monitor and improve the quality of the electric power before it reaches consumers.
Finally, electricity is delivered to homes and businesses, where its consumption is measured by electric meters. Modern power grids use advanced technology, such as automation and real-time monitoring, to ensure efficient and reliable distribution of electricity.
Glossary and common terms
Below we show you a glossary that includes basic and advanced concepts to understand the world of electrical energy.
 Alternator: Device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current.
Alternator: Device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of alternating current.- Ampere (A): Unit of measurement of electric current. Represents the amount of electric charge that passes through a point in one second.
- Battery: Device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy when necessary.
- Coil: Component of an electrical circuit that generates a magnetic field when current passes through it.
- Alternating current (AC): A type of electric current in which the direction of electron flow changes periodically.
- Direct current (DC): A type of electric current in which electrons flow in only one direction.
- Capacitor: Component that stores electrical energy in an electric field, releasing it when needed.
- Circuit breaker: Safety device that cuts off the power supply when it detects an abnormal or excessive current.
- Diode: Electronic component that allows the passage of current in only one direction.
- Energy efficiency: Relationship between the amount of useful energy obtained and the total energy used.
- Electron: Subatomic particle with a negative charge, essential for the flow of electric current.
- Phase: In alternating current, refers to the state of a current cycle at a specific point in time.
- Fuse: Safety device that protects an electrical circuit by melting when the current exceeds a certain level.
- Generator: Machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Load graph: Visual representation of the consumption of electrical energy in a given period.
- Hertz (Hz): Unit of frequency that measures the number of cycles per second in an alternating current.
- Hydroelectricity: Electrical energy produced from the movement of water.
- Impedance: Total resistance that a circuit presents to the passage of alternating current, considering both electrical resistance and reactance.
- Inverter: Device that converts direct current into alternating current.
- Joule (J): Unit of energy representing the amount of work done when a current of one ampere flows through a resistance of one ohm for one second.
- Kilowatt (kW): Unit of power equivalent to one thousand watts.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): Unit of energy that represents the consumption of one kilowatt of power for one hour.
- Transmission line: Set of conductors that transport electrical energy from generating plants to consumption centers.
- Light: Visible manifestation of electromagnetic energy, which can be generated by electrical devices such as light bulbs.
- Megawatt (MW): Unit of power equivalent to one million watts.
- Electric motor: Device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Neutral: Conductor in an electrical system that carries current back to the source, normally connected to ground.
- Node: Point in an electrical system where several lines or equipment are connected.
- Ohm (Ω): Unit of electrical resistance that measures opposition to the flow of current.
- Electromagnetic waves: Energy that propagates through space in the form of waves, including visible light and radio waves.
- Electrical power: Rate at which electrical energy is consumed or generated, measured in watts.
- Solar panel: Device that converts sunlight into electrical energy.
- Resistance: Component that opposes the flow of electric current, converting part of the energy into heat.
- Power grid: Distribution system that transports electricity from power plants to end consumers.
- Substation: Facility that reduces or increases the voltage of electrical energy for its distribution or transmission.
- Renewable energy system: Set of technologies that generate electrical energy from renewable sources such as wind, sun or water.
- Transformer: Device that alters the voltage of the electric current, increasing or decreasing its level.
- Electrical tension (Voltage): Difference in electrical potential between two points, which drives the flow of current.
- Volt (V): Unit of measurement of voltage or electrical tension.
- Watt (W): Unit of power that measures the rate of consumption or generation of electrical energy.
- Wattmeter: Device used to measure the electrical power consumed or generated.
- Watt-hour (Wh): Unit of energy that measures the work performed or energy consumed in one hour.
- Load zone: Geographic area where the demand for electrical energy is controlled and distributed.