
Atomic energy, also known as nuclear energy, is one of the most powerful and, at the same time, most controversial sources of energy today. To understand its importance and how it is harnessed, it is essential to understand its physical basis, which lies in the nucleus of atoms.
The atomic nucleus and energy
 Atomic energy comes from the interactions within the nucleus of atoms. An atom is made up of a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit it. Atomic energy is based on two fundamental processes: nuclear fission and fusion.
Atomic energy comes from the interactions within the nucleus of atoms. An atom is made up of a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit it. Atomic energy is based on two fundamental processes: nuclear fission and fusion.
- Nuclear fission : This process occurs when a heavy atom, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, splits into two smaller atoms when bombarded by a neutron. This process releases a large amount of energy, which manifests itself as heat. The heat generated is used to produce steam, which, in turn, drives turbines and generates electricity. Fission is the basis of today's nuclear power plants.
- Nuclear fusion : This process occurs when two light atoms, usually hydrogen isotopes such as deuterium and tritium, combine to form a heavier atom. Nuclear fusion releases even more energy than fission, but it has not yet been efficiently controlled to produce energy on a large scale.
The concept of energy in physics
In the context of physics, energy is defined as the capacity to do work. There are different forms of energy, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, and nuclear. Nuclear energy, in particular, is associated with the strong nuclear force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature, which holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of atoms.
When atoms split (fission) or combine (fusion), massive amounts of energy are released. Einstein's famous formula, E=mc², explains how this energy is produced. According to this equation, energy (E) equals mass (m) multiplied by the speed of light squared (c²). This implies that a small amount of mass can be converted into an enormous amount of energy. This principle is crucial to understanding why nuclear energy is so efficient.
Applications of atomic energy
Nuclear energy has a variety of applications beyond electricity generation. These include:
Atomic energy has a wide variety of applications that directly impact various fields of science, technology, and medicine.
Electricity generation
Among the most notable is its use in electricity generation. Through nuclear fission, large amounts of energy are released by splitting the nuclei of heavy atoms like uranium, generating heat to produce steam and, in turn, generate electricity in nuclear power plants.
This energy source is efficient and capable of providing large amounts of electricity in a continuous and stable manner.
Medicine
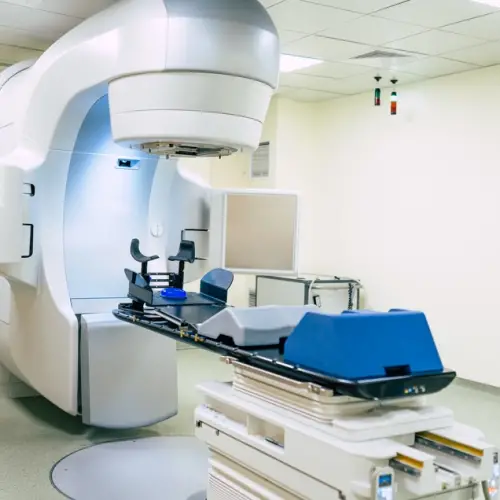 In the field of medicine, atomic energy has a significant impact, especially in the treatment of cancer.
In the field of medicine, atomic energy has a significant impact, especially in the treatment of cancer.
Radiation therapy uses nuclear radiation to destroy tumor cells, allowing for more precise and effective treatments. In addition, radioactive isotopes are used in medical diagnostics, in procedures such as positron emission tomography (PET) and radionuclide scanning, to obtain detailed images of the interior of the human body.
Scientific research
Scientific research also benefits from atomic energy.
Particle accelerators use nuclear energy to study subatomic particles and better understand the fundamental laws of physics. These advances are crucial for the development of new theories in fields such as particle physics and astrophysics.
Propulsion and transportation
In the field of propulsion, nuclear reactors are essential in submarines and aircraft carriers, providing a long-lasting and efficient source of power.
These vehicles can operate for long periods without refueling, giving them a strategic advantage in terms of range.
The risks of nuclear energy
 Despite its benefits, nuclear energy poses significant challenges. Chief among these is the management of radioactive waste, which can remain hazardous for thousands of years. Furthermore, nuclear accidents, such as those at Chernobyl and Fukushima, have raised serious concerns about the risks associated with this energy source.
Despite its benefits, nuclear energy poses significant challenges. Chief among these is the management of radioactive waste, which can remain hazardous for thousands of years. Furthermore, nuclear accidents, such as those at Chernobyl and Fukushima, have raised serious concerns about the risks associated with this energy source.
In the long term, the future of nuclear energy is also determined by advances in nuclear fusion, which could offer a much cleaner and more abundant source of energy than fission.
Differences between atomic energy and nuclear energy

Atomic energy and nuclear energy are terms often used interchangeably, but there is a slight difference in their scope and how they are used in different contexts.
Atomic energy primarily refers to the energy released through nuclear reactions, such as nuclear fission and fusion. The term "atomic energy" is more commonly used when referring to the practical applications of this energy, such as in nuclear power plants to generate electricity or in medical applications, such as radiation therapy. In this context, it refers to the harnessing of the energy obtained from atoms and their nuclei.
On the other hand, the concept of nuclear energy is broader and refers to the energy stored in the nucleus of atoms and the nuclear reactions (fission or fusion) that release this energy. Nuclear energy includes both atomic energy and other energy applications not necessarily oriented toward direct consumption, such as research or nuclear research reactors.
It is also sometimes used to refer to nuclear technology in general, such as nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.