
The use of nuclear energy in civil applications carries a series of significant benefits for society. Mainly, its fundamental role in the generation of electricity is highlighted, where nuclear power plants play an essential role. These facilities take advantage of the splitting of uranium atom nuclei in nuclear reactors to efficiently produce electricity.
Despite being the subject of controversy, especially in relation to the risks of nuclear accidents, it is crucial to recognize the multiple benefits derived from nuclear technology. Below are some of the advantages that this technology brings to society.
1. Electricity generation
A nuclear power plant produces energy from the fission reactions of uranium nuclei. Nuclear fission reactions generate a large amount of thermal energy that can later be transformed into electricity. This conversion process is carried out in nuclear power plants.
Obtaining electricity on demand
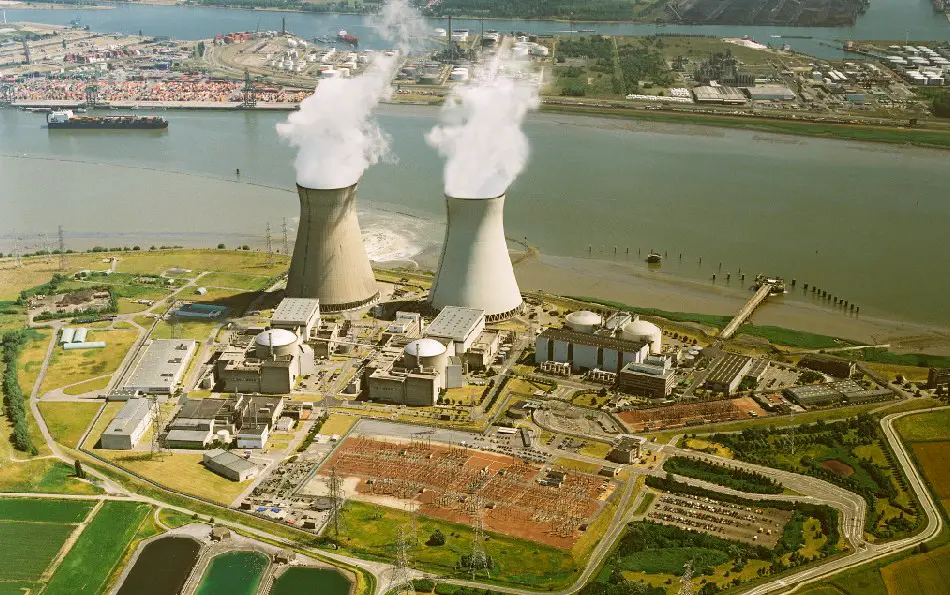 The main benefit of generating electricity through atomic energy compared to most renewable energies is that electrical production can be regulated over time.
The main benefit of generating electricity through atomic energy compared to most renewable energies is that electrical production can be regulated over time.
This means that depending on the electrical demand, those responsible for nuclear plants can increase or decrease the power of the nuclear reactor.
On the other hand, energy production through renewable energies depends on factors such as schedules, climatic factors, etc. For example, during night hours or cloudy days solar energy cannot produce electricity. In the case of wind energy, this depends on the intensity of the wind, which may or may not coincide with the demand at a given time.
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions
Remaining fossil fuel resources are limited, so if all energy generation continued to be based on coal, natural gas or oil, as resources decline, prices will rise to unsustainable levels.
Greater energy efficiency per unit of fuel
Nuclear energy has the advantage that the nuclear fuel used, generally enriched uranium or plutonium, offers great performance. With very little uranium you can obtain a large amount of energy. This represents savings in raw materials but also in transportation, extraction and handling of nuclear fuel. The cost of nuclear fuel (generally uranium) represents 20% of the cost of the energy generated.
Work is currently underway on the development of nuclear fusion which would further increase efficiency and reduce the risk of radioactive leaks.
2. Environmental benefits
The benefits of nuclear energy in environmental terms are significant when compared to the disadvantages of thermal power plants.
The advantages of nuclear energy compared to the production of electricity using fossil fuels are mainly concentrated in the environmental aspect. Thermal power plants that use coal or natural gas to drive their steam turbines generate a large amount of greenhouse gases. The polluting gases that come out of the plants promote the greenhouse effect and therefore contribute to increasing the global warming of the planet.
How does global warming occur?
The solar radiation that reaches Earth contains a large amount of energy. Part of this energy is used to heat the planet and another part is reflected back outside as if it were a mirror. In part, it is important that part of this heat stays on Earth since if this did not happen the planet would freeze.
What happens with pollution is that greenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere making a layer. When the radiation has been reflected from the Earth and returns to outer space, it hits this contaminating layer and partially returns to the Earth again. For this reason, the Earth heats up excessively.
3. Medical applications
 Another notable advantage of nuclear energy lies in its relevant role in fields as important as nuclear medicine. This area takes advantage of radioactive isotopes and other aspects related to atomic energy to prevent, diagnose, treat and investigate various medical conditions.
Another notable advantage of nuclear energy lies in its relevant role in fields as important as nuclear medicine. This area takes advantage of radioactive isotopes and other aspects related to atomic energy to prevent, diagnose, treat and investigate various medical conditions.
Radiopharmaceuticals, used in clinical applications, cover virtually all medical specialties. Currently, most hospitals and health centers have Departments of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, using radiochemical methods for the diagnosis and investigation of a wide variety of diseases. This diversified use underlines the versatility and importance of nuclear energy for the benefit of human health.