
A nuclear reactor (or atomic reactor) is a facility capable of converting nuclear energy into thermal energy. The reactors have the capacity to initiate, control and maintain the nuclear chain reactions that occur in the core of this facility.
In a common nuclear power plant, nuclear reactors are used to produce thermal energy and generate water vapor to drive the steam turbines with which it is obtained.
Basic operation
 A nuclear reactor generates energy through nuclear fission, a process in which the nuclei of heavy atoms, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, are split into smaller fragments when bombarded by neutrons. This splitting releases a huge amount of energy in the form of heat.
A nuclear reactor generates energy through nuclear fission, a process in which the nuclei of heavy atoms, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, are split into smaller fragments when bombarded by neutrons. This splitting releases a huge amount of energy in the form of heat.
The reactor contains a core with nuclear fuel, usually in the form of fuel rods. The initiating neutrons collide with the fuel atoms, causing them to fission and releasing more neutrons and energy. These released neutrons cause more fissions in a controlled chain reaction.
To manage this reaction, the reactor has control rods made of materials that absorb neutrons, such as boron or cadmium. By adjusting the position of these bars, you can speed up, slow down or stop the chain reaction.
The heat generated in the reactor core warms a coolant, typically water, that circulates through the core. This coolant transfers the heat to a steam generator, where high-pressure steam is produced. The steam drives a turbine connected to an electric generator, producing electricity.
What is a nuclear reactor used for?
A nuclear reactor is primarily used to generate electrical energy through a process called controlled nuclear fission. Nuclear power plants are facilities designed to use nuclear reactors for this purpose.
However, atomic reactors exist to fulfill other objectives. Here are some uses and benefits of nuclear reactors:
Electric power generation
Nuclear reactors are a continuous source of electrical energy. Nuclear fission produces a large amount of heat, which is used to generate steam and drive turbines that, in turn, generate electricity.
One of the main advantages that atomic reactors provide is that they can operate for long periods without interruption. In this way, they can provide a constant source of base energy to meet electrical demand.
Radioisotope production
Nuclear reactors are also used for the production of radioisotopes used in medicine, research and industrial applications.
Some radioisotopes have unique properties that are used in medical diagnostics and treatments, such as diagnostic imaging and radiation therapy.
Scientific and technological research
Nuclear reactors play a crucial role in scientific research and technological development.
Research reactors are used to:
-
Study the physics of atomic nuclei.
-
Carry out research on nuclear materials.
-
Simulate extreme conditions.
-
Analyze security.
-
Improve and develop new reactor designs.
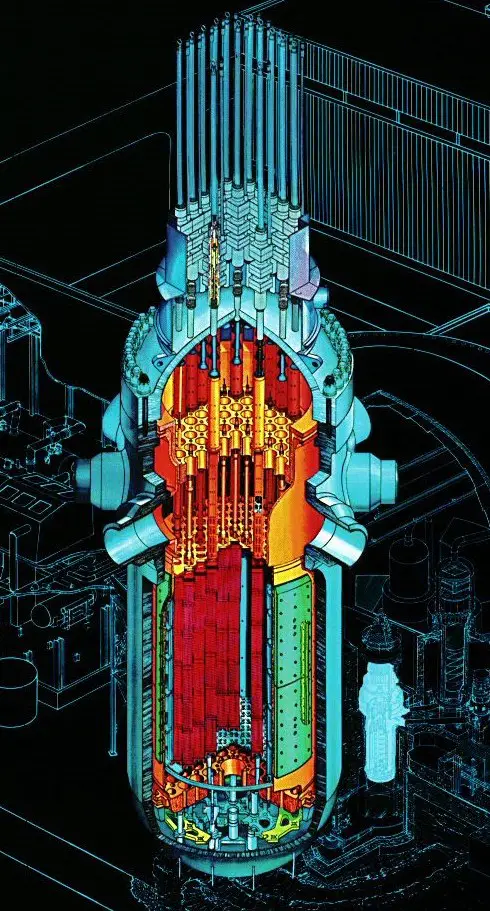
Parts of a nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is made up of the following components:
1. Núcleo
It consists of fuel rods. The reactor core has a characteristic geometric shape. The core is cooled by a fluid, usually water.
In some nuclear reactors the core is located inside a pool of water, about 10 to 12 meters deep, or inside a pressure vessel made of steel.
2. Fuel rods
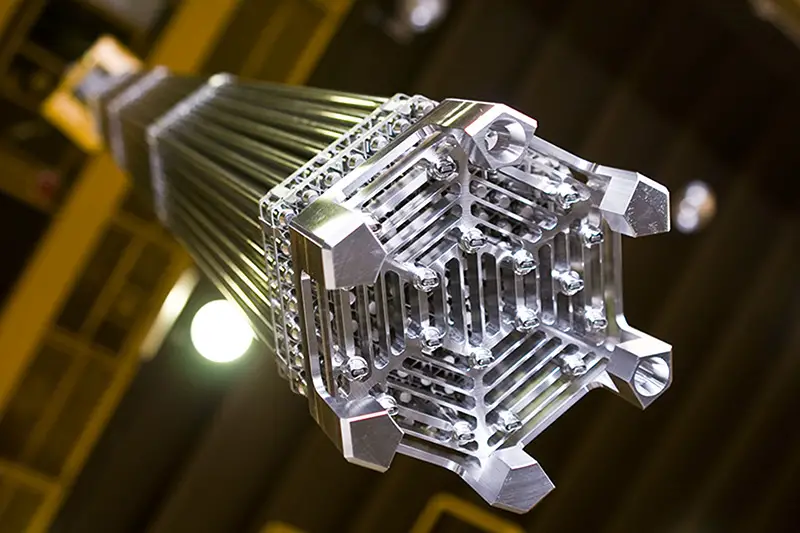

They are the physical place where the nuclear fuel is confined. Some fuel rods contain uranium mixed with aluminum in the form of flat sheets. These sheets are separated by a certain distance that allows the circulation of heat dissipating fluid.
The sheets are placed in a type of box that serves as a support.
Nuclear fuel is a material capable of fissioning sufficiently to reach critical mass, that is, to sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is placed in such a way that the thermal energy produced by this nuclear reaction can be rapidly extracted.
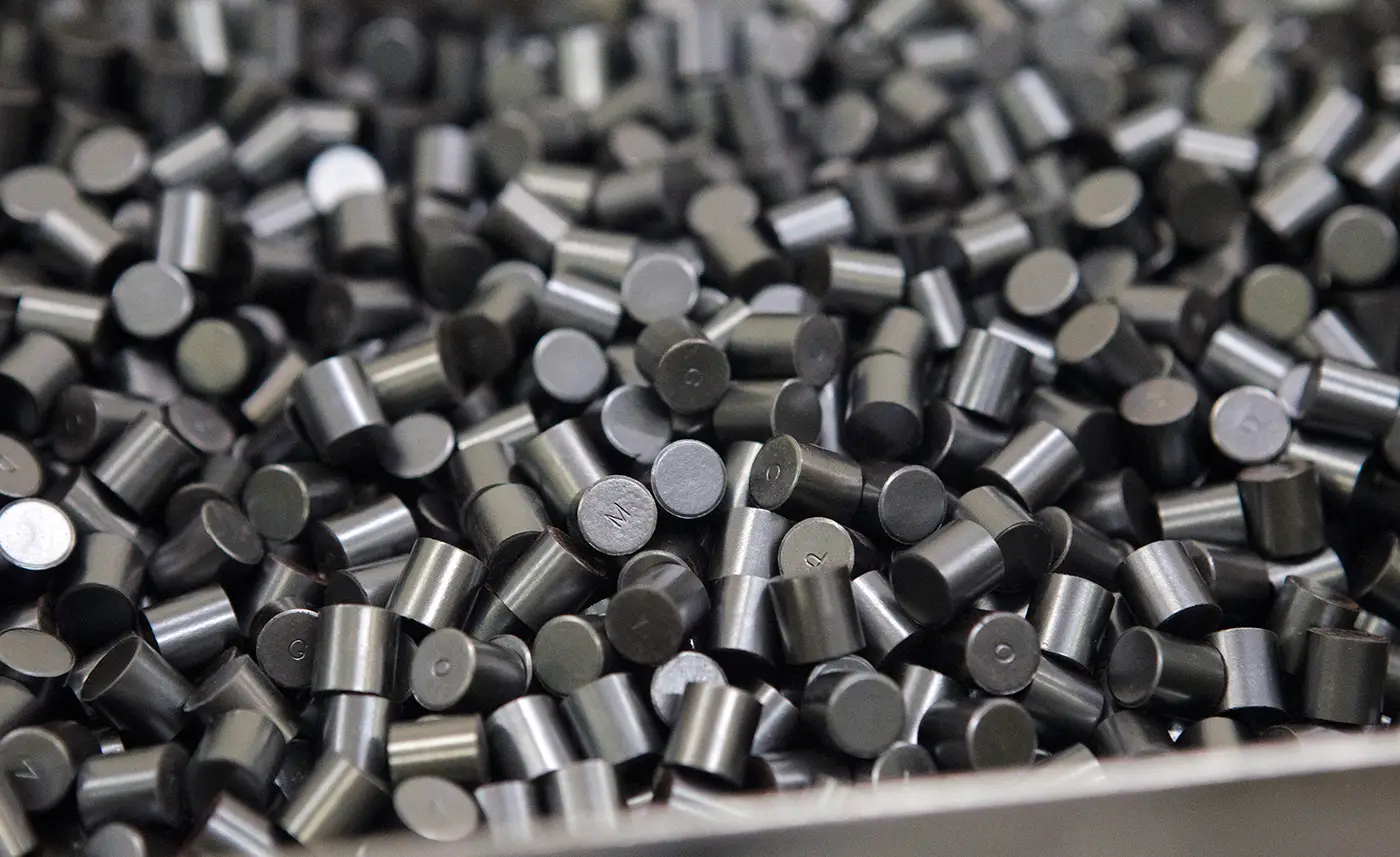 Solid nuclear fuel is used in nuclear power plants. Nuclear fuels vary depending on the type of reactor but generally uranium derivatives are used.
Solid nuclear fuel is used in nuclear power plants. Nuclear fuels vary depending on the type of reactor but generally uranium derivatives are used.
Natural uranium is extracted from uranium mines but is not radioactive enough to be used directly in a reactor. Natural uranium undergoes an enrichment process to obtain more unstable isotopes to increase the coefficient of reactivity.
For a nuclear reactor to operate for a period of time, it must have excess reactivity, which is maximum with fresh fuel and decreases with its life until it is eliminated. At this moment the recharging of the nuclear fuel is carried out.
3. Control bars
Control rod bundles provide a rapid means of controlling chain reactions. These bars allow for rapid power changes in the nuclear reactor and its eventual shutdown in case of emergency.
Control rods are made of neutron absorbing materials and typically have the same dimensions as the fuel elements.
The core's reactivity coefficient is increased or decreased by raising or lowering the control rods. Raising or lowering the control rods changes the amount of neutron-absorbing material contained in them in the core.
In normal operation, a nuclear reactor has the control rods fully or partially removed from the core.
The design of nuclear power plants is such that in the event of a failure in a safety or control system of the reactor, it always acts in the direction of maximum safety, completely inserting all the control rods into the reactor core.
This action brings the nuclear reactor to a safe stop within a few seconds.
4. Nuclear moderator
Neutrons resulting from a nuclear fission reaction have high kinetic energy. The higher their speed, the less likely they are to fission other atoms, so it is advisable to reduce this speed to encourage new chain reactions.
The function of the moderator is to reduce the kinetic energy of the neutrons through elastic collisions of the neutrons with the nuclei of the moderator itself.
Among the most used moderators are light water, heavy water and graphite.
5. Soda
In order to take advantage of the thermal energy released by nuclear fission reactions, a coolant is used. The function of the coolant is to absorb this thermal energy and transport it.
The coolant must be anti-corrosive, with a high heat capacity and must not absorb neutrons.
The most common refrigerants are:
-
Gases such as carbon dioxide and helium
-
Liquids such as light water and heavy water.
-
There are even some organic compounds and liquid metals such as sodium, which are also used for this function.
6. Reflector
In a nuclear chain reaction, a certain number of neutrons tend to escape from the region where the reaction is taking place. This neutron leakage can be minimized by the existence of a reflecting medium that redirects the neutrons back into the reaction region.
The reflecting medium surrounding the core must have a low effective capture section so as not to reduce the number of neutrons and so that as many of them as possible are reflected.
7. Shielding
When a nuclear reactor is in operation, a large amount of radiation is generated . Shielding is used to protect and isolate the facility's workers from the radioactivity caused by fission products.
Biological shielding is therefore placed around the reactor to intercept these radioactive emissions.
The most commonly used materials to build this shielding are concrete, water and lead.
Types of reactors
There are several types of nuclear reactors, some of which are:
- Pressurized water reactor (PWR): In a PWR, water is used as a coolant and moderator. High-pressure water circulates through the reactor core to transfer heat produced by nuclear reactions. It is the most common type of reactor in commercial nuclear power plants.
- Boiling Water Reactor (BWR): In a BWR, water is used as both a coolant and a moderator. Water boils in the core and the steam generated drives turbines to generate electricity.
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (CANDU): In these reactors, the moderator is heavy water (deuterium oxide) and the coolant is light water. They are known for their flexibility and ability to use natural uranium as fuel.
- Molten Salt Reactor (MSR): In an MSR, nuclear fuel is dissolved in a molten salt that serves as a coolant. They are known for their inherent safety and ability to operate at high temperatures.
- Metal-cooled fast reactor (LMFR): These reactors use liquid metals, such as sodium or lead, as coolants and operate at faster neutron speeds. They are efficient at transmuting nuclear waste and producing more fuel.
- Heavy Water Graphite Reactor (HWGCR): This type of reactor uses graphite as a moderator and heavy water as a coolant. They are known for their use in plutonium production.
- Fast Neutron Reactor (FNR): Fast neutron reactors operate with fast rather than moderate neutrons. They are efficient in the use of fuel and the production of new nuclear materials.