
Chemical elements are the basic units of matter. They are made up of atoms that contain a specific number of protons in their nucleus, known as the atomic number. This number is unique to each element and defines its chemical and physical properties.
Elements are grouped together on the periodic table, which organizes these elements by their characteristics and behaviors. They can also combine with each other through chemical reactions to form compounds with new properties, such as when oxygen and hydrogen combine to form water.
Definition of element in chemistry
 A chemical element is a pure substance composed of atoms that have the same number of protons in their nucleus, known as the atomic number. This number distinguishes each element and is the characteristic that defines it.
A chemical element is a pure substance composed of atoms that have the same number of protons in their nucleus, known as the atomic number. This number distinguishes each element and is the characteristic that defines it.
The term "chemical species" is also used to refer to an atom, although it can also refer to molecules, ions, and other substances.
Each element has a chemical symbol, composed of one or two letters, and a name that is generally derived from Latin. These symbols and names are regulated by the IUPAC and are reflected in Mendeleev's periodic table.
Elements and simple substances
When chemical elements exist in isolation, they are known as simple substances.
It is important to distinguish between chemical elements, which are abstract entities described by their characteristics, and material objects, which are substances that actually exist in nature. The latter can be simple chemical compounds with well-defined physical and chemical properties.
Noble gases
Within the chemical elements, a particular group is the noble gases.
These elements share very similar properties: they are monatomic, colorless, odorless gases and have extremely low chemical reactivity. Examples of noble gases include helium, neon and argon.
Combination of elements
 Chemical elements can react with each other to form new compounds, a process that occurs in chemical reactions.
Chemical elements can react with each other to form new compounds, a process that occurs in chemical reactions.
For example, oxygen and hydrogen, two gaseous elements, can combine to form water, a compound with completely different properties from its constituent elements.
How many chemical elements are there?
There are 118 known chemical elements, of which 94 are found in nature (some only in small quantities). The remaining 24 are obtained artificially as a result of nuclear reactions. These elements are essential in scientific research and in various technological applications.
Isotopes
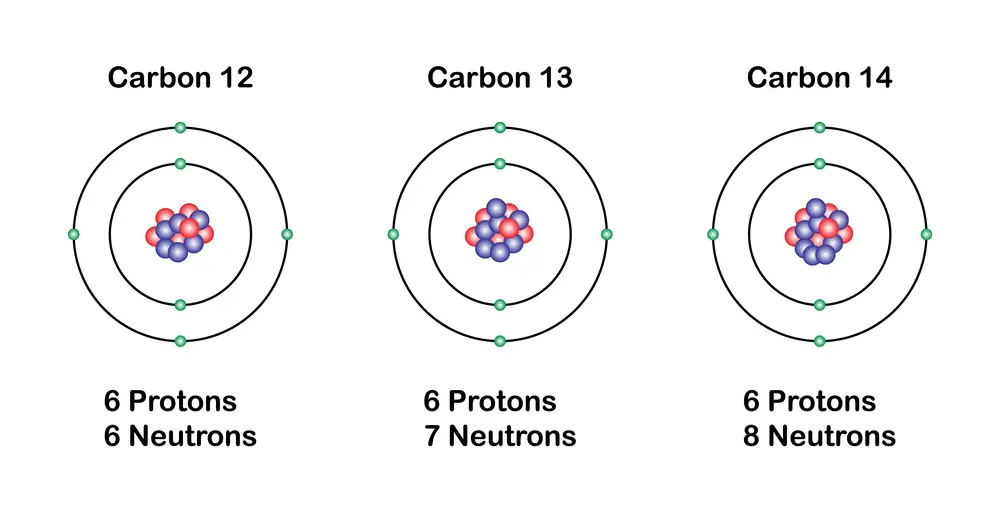 An important aspect of the elements is the existence of isotopes, which are variants of the same chemical element.
An important aspect of the elements is the existence of isotopes, which are variants of the same chemical element.
Isotopes have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This causes them to have different atomic masses. Although isotopes of an element have similar chemical properties, their physical properties (such as stability and radioactivity) can vary considerably.
For example, carbon has two stable isotopes, carbon-12 and carbon-13, and one radioactive isotope, carbon-14, which is used in archaeological dating.
Isotopes in the nuclear industry
Some isotopes are essential in nuclear applications, especially in nuclear reactors . Below I show you the most important ones:
- Uranium-235 (U-235) : One of the most important isotopes in nuclear reactors. Its ability to fission when bombarded with neutrons makes it a crucial fuel for nuclear power generation. Uranium-235 is found in very small concentrations in nature, so it must be enriched to be used in reactors.
- Plutonium-239 (Pu-239) : This isotope is produced in nuclear reactors from Uranium-238. When Uranium-238 absorbs a neutron, it becomes Plutonium-239, which is also fissile and can be used as fuel in nuclear reactors.
- Deuterium (H-2) : An isotope of hydrogen found in water and used in nuclear fission reactors. Deuterium, along with tritium (H-3), is used in experimental fusion reactors, where hydrogen isotopes are fused to release energy.
- Tritium (H-3) : Although it is radioactive and has a short half-life, Tritium is an isotope used in certain types of nuclear fusion reactors. This isotope is produced artificially and is used in nuclear fusion experiments, such as those conducted in the ITER fusion reactors.
Classification of elements
Chemical elements are classified into metals, non-metals and metalloids, depending on their properties.
Metals, which make up the majority of elements, are good conductors of electricity and heat, while nonmetals tend to be insulators. Metalloids, on the other hand, have properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
In the periodic table, elements are arranged in rows called periods and columns called groups. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties.
What does the name of the elements depend on?
The right to propose a name for a new chemical element belongs to its discoverers.
However, this name must comply with certain rules. After a new discovery is published, its existence must be verified by independent laboratories. If confirmed, the IUPAC officially approves the name of the new element.
Currently, all 118 known elements have permanent names approved by IUPAC, and before the final name is approved, temporary names based on their atomic number are used.
Classification of elements in the periodic table
The chemical elements are classified in the periodic table of elements.
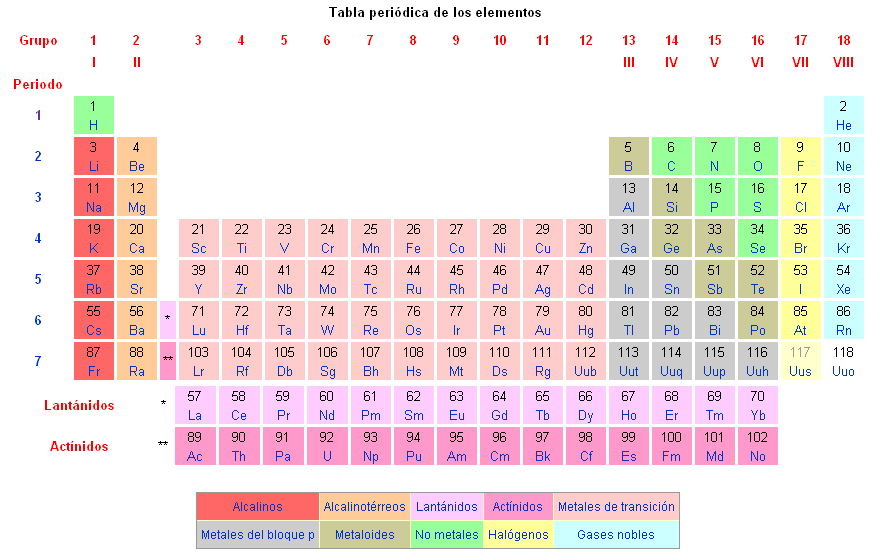
The known chemical elements are the following:
|
Chemical element |
Symbol |
Atomic number (Z) |
Atomic weight (u) |
|
Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
1.0079 |
|
Helium |
He |
2 |
4.0026 |
|
Lithium |
Li |
3 |
6941 |
|
Beryllium |
Be |
4 |
9.0122 |
|
Boron |
B |
5 |
10811 |
|
Carbon |
C |
6 |
12.0107 |
|
Nitrogen |
N |
7 |
14.0067 |
|
Oxygen |
EITHER |
8 |
15.9994 |
|
Fluorine |
F |
9 |
18.9984 |
|
Neon |
No |
10 |
20.1797 |
|
Sodium |
Na |
11 |
22.9897 |
|
Magnesium |
Mg |
12 |
24305 |
|
Aluminum |
To the |
13 |
26.9815 |
|
Silicon |
Yeah |
14 |
28.0855 |
|
Phosphorus |
P |
15 |
30.9738 |
|
Sulfur |
S |
16 |
32065 |
|
Chlorine |
Cl |
17 |
35453 |
|
Argon |
Ar |
18 |
39948 |
|
Potassium |
K |
19 |
39.0983 |
|
Calcium |
AC |
20 |
40078 |
|
Scandium |
Sc |
21 |
44.9559 |
|
Titanium |
You |
22 |
47867 |
|
Vanadium |
V |
23 |
50.9415 |
|
Chrome |
Cr |
24 |
51.9961 |
|
Manganese |
Mn |
25 |
54938 |
|
Iron |
Faith |
26 |
55845 |
|
Cobalt |
Co |
27 |
58.9332 |
|
Nickel |
Neither |
28 |
58.6934 |
|
Copper |
Cu |
29 |
63546 |
|
Zinc |
Zn |
30 |
65.39 |
|
Gallium |
Ga |
31 |
69723 |
|
Germanium |
Ge |
32 |
72.64 |
|
Arsenic |
Ace |
33 |
74.9216 |
|
Selenium |
HE |
34 |
78.96 |
|
Bromine |
Br |
35 |
79904 |
|
Krypton |
Kr |
36 |
83.8 |
|
Rubidium |
Rb |
37 |
85.4678 |
|
Strontium |
Mr |
38 |
87.62 |
|
Yttrium |
AND |
39 |
88.9059 |
|
Zirconium |
Zr |
40 |
91224 |
|
Niobium |
Nb |
41 |
92.9064 |
|
Molybdenum |
Mo |
42 |
95.94 |
|
Technetium |
Tc |
43 |
98 |
|
Ruthenium |
Ru |
44 |
101.07 |
|
Rhodium |
Rh |
45 |
102.9055 |
|
Palladium |
P.S |
46 |
106.42 |
|
Silver |
Ag |
47 |
107.8682 |
|
Cadmium |
CD |
48 |
112411 |
|
Indian |
In |
49 |
114818 |
|
Tin |
Sn |
50 |
118.71 |
|
Antimony |
Sb |
51 |
121.76 |
|
Tellurium |
Tea |
52 |
127.6 |
|
Iodine |
Yo |
53 |
126.9045 |
|
Xenon |
Xe |
54 |
131293 |
|
Cesium |
Cs |
55 |
132.9055 |
|
Barium |
Ba |
56 |
137327 |
|
Lanthanum |
The |
57 |
138.9055 |
|
Cerium |
EC |
58 |
140116 |
|
Praseodymium |
Pr |
59 |
140.9077 |
|
Neodymium |
Nd |
60 |
144.24 |
|
Promethium |
P.m |
61 |
145 |
|
Samarium |
YE |
62 |
150.36 |
|
Europium |
I |
63 |
151964 |
|
Gadolinium |
Gd |
64 |
157.25 |
|
Terbium |
Also |
65 |
158.9253 |
|
Dysprosium |
Dy |
66 |
162.5 |
|
Holmium |
Ho |
67 |
164.9303 |
|
Erbium |
It is |
68 |
167259 |
|
Thulium |
Tm |
69 |
168.9342 |
|
Ytterbium |
Yb |
70 |
173.04 |
|
Lutetium |
Lu |
71 |
174967 |
|
Hafnium |
Hf |
72 |
178.49 |
|
Tantalum |
Ta |
73 |
180.9479 |
|
Tungsten |
W |
74 |
183.84 |
|
Rhenium |
Re |
75 |
186207 |
|
Osmium |
You |
76 |
190.23 |
|
Iridium |
Go |
77 |
192217 |
|
Platinum |
Pt |
78 |
195078 |
|
Gold |
Au |
79 |
196.9665 |
|
Mercury |
Hg |
80 |
200.59 |
|
Thallium |
Tl |
81 |
204.3833 |
|
Lead |
Pb |
82 |
207.2 |
|
Bismuth |
Bi |
83 |
208.9804 |
|
Polonium |
Po |
84 |
209 |
|
Astatine |
At |
85 |
210 |
|
Radon |
Rn |
86 |
222 |
|
Francium |
Fr |
87 |
223 |
|
Radio |
Ra |
88 |
226 |
|
Actinium |
Ac |
89 |
227 |
|
Thorium |
Th |
90 |
232.0381 |
|
Protactinium |
Pa |
91 |
231.0359 |
|
Uranium |
OR |
92 |
238.0289 |
|
Neptunium |
Np |
93 |
237 |
|
Plutonium |
Pu |
94 |
244 |
|
Americium |
A.M |
95 |
243 |
|
Curium |
Cm |
96 |
247 |
|
Berkelium |
Bk |
97 |
247 |
|
Californium |
Cf |
98 |
251 |
|
Einsteinium |
Is |
99 |
252 |
|
Fermium |
Fm |
100 |
257 |
|
Mendelevium |
Md |
101 |
258 |
|
Nobelium |
No |
102 |
259 |
|
Laurentius |
Lr |
103 |
262 |
|
Rutherfordium |
Rf |
104 |
261 |
|
Dubnium |
Db |
105 |
262 |
|
Seaborgium |
Sg |
106 |
266 |
|
Bohrio |
Bh |
107 |
264 |
|
Hassio |
Hs |
108 |
277 |
|
Meitnerium |
Mt |
109 |
268 |
|
Darmstadtium |
Ds |
110 |
281 |
|
Roentgenium |
Rg |
111 |
272 |
|
Copernicium |
Cn |
112 |
285 |
|
Nihonium |
Nh |
113 |
286 |
|
Flerovium |
Fl |
114 |
289 |
|
Moscovium |
Mc |
115 |
288 |
|
Livermorium |
Lv |
116 |
292 |
|
Teneso |
Ts |
117 |
294 |
|
Oganesson |
Og |
118 |
294 |
Representation of a chemical element
Symbols of chemical elements are used as abbreviations for the name of elements. As a symbol, they usually take the initial letter of the name of the element and, if necessary, add the next one or one of the following. Usually these are the initial letters of the Latin names of the elements.
 Such a system of chemical symbols was proposed in 1814 by the Swedish chemist J. Berzelius. The elements used before the official adoption of their permanent names and symbols consisted of three letters, meaning the Latin names of the three digits in the decimal notation of their atomic number. The notation system for higher homologues described above (Eka-Rn, Eka-Pb, etc.) is also used.
Such a system of chemical symbols was proposed in 1814 by the Swedish chemist J. Berzelius. The elements used before the official adoption of their permanent names and symbols consisted of three letters, meaning the Latin names of the three digits in the decimal notation of their atomic number. The notation system for higher homologues described above (Eka-Rn, Eka-Pb, etc.) is also used.
The smaller numbers next to the element symbol indicate:
-
Atomic mass at top left.
-
Atomic number at bottom left.