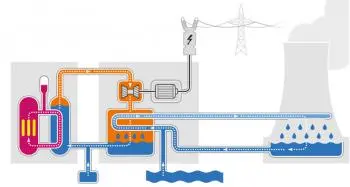
The operation of a nuclear power plant is similar to that of any other thermal power plant. Actually, a nuclear plant is a type of thermal power plant whose function is to generate electrical energy.
There are several types of power plants, but the principle of operation is as follows:
-
Generate nuclear reactions to obtain thermal energy.
-
Second, generate water vapor with thermal energy.
-
Third, drive a steam turbine generator to get mechanical energy and ultimately electricity.
A nuclear power plant is a facility where the entire process is carried out. The most crucial difference from the other thermal power plants is the way of obtaining thermal energy. In a nuclear plant, heat is generated from uranium fuel atomic reactors.
Obtaining heat: What is a nuclear reaction?
A nuclear reaction is an alteration in the nucleus of an atom that produces heat in a process called fission.
Atoms are composed of a combination of sub-particles: protons and neutrons. These sub-particles are linked by force bonds that possess a large amount of energy.
When these bonds are broken, so-called fission products are generated, which are radioactive materials and a considerable amount of energy emission.
Types of nuclear power plants
Worldwide, 90% of power plants use light water reactors. There are two types of light water reactors:
-
Nuclear pressurized water reactor (PWR).
-
Boiling water nuclear reactor (BWR).
Among these two types of reactor, the pressurized water reactor is the most widely used in the world.
How does a pressurized water nuclear power plant work?
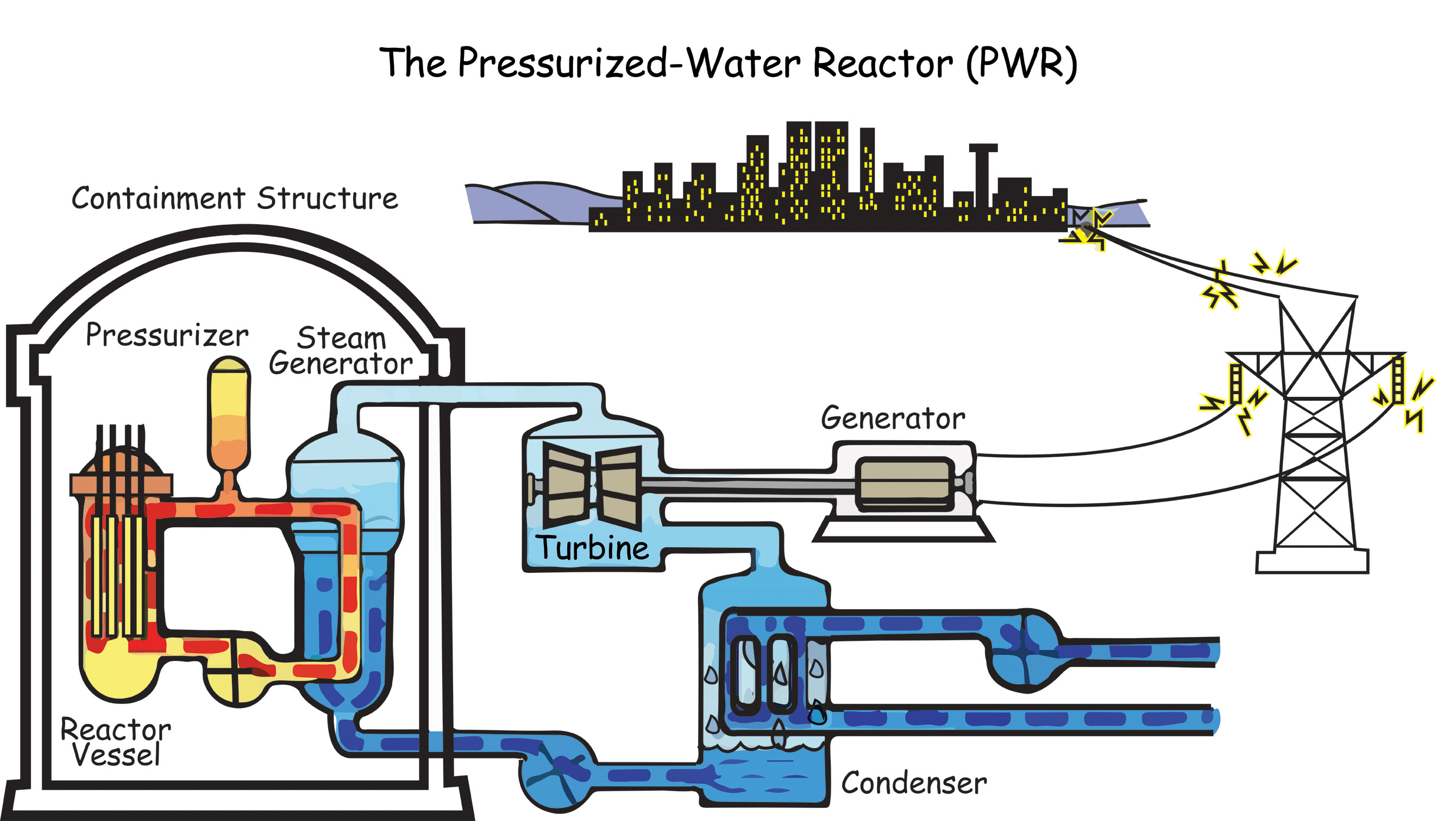
The basic operation of a nuclear power plant with a PWR reactor can be simplified into four steps:
-
Obtaining thermal energy through nuclear fission of the nucleus of fuel atoms.
-
Generate water vapor using the thermal energy obtained in the previous step.
-
Drive a set of turbines using the water vapor obtained.
-
Harnessing the mechanical energy of the turbines to drive an electric generator to produce electricity.
From a physical point of view, several energy changes are observed in this reactor operation:
Initially, we have nuclear energy (the one that keeps the nuclei of the atoms cohesive). Subsequently, when it breaks, it is converted into thermal energy that is used to generate steam.
The thermal energy becomes the internal energy of the water (now steam). Finally, the water's internal energy and heat energy are transformed into kinetic energy by driving the turbine.
Finally, the generator converts kinetic energy into electrical energy.
water circuits
Nuclear power plants that work with a pressurized water reactor have two water circuits:
-
The primary circuit that passes through the reactor.
-
The secondary circuit that passes through the steam turbines.
In the primary circuit, the water is subjected to high pressure. As a result, nuclear reactions heat water when passing through and acquire a very high temperature and the pressure prevents it from gasifying.
The secondary circuit is also closed. The water in this circuit is heated by being in thermal contact with the primary circuit to convert it into steam and drive the turbine.
Finally, it is cooled by thermal contact with an external water source.
What happens in the nuclear reactor?
The nuclear reactor is the plant's most sensitive and most important part.
The reactor is responsible for converting nuclear energy into thermal energy. Inside, nuclear fuel rods are placed, generally made of uranium, a very unstable element in the periodic table.
The simple impact of a neutron against a uranium atom causes its breakage, leading to a nuclear fission reaction. Each nuclear fission results in two pieces of radioactive material and one or two more neutrons. These neutrons can collide with atoms and generate chain reactions.
If these reactions are not controlled, more and more reactions will occur per second. Finally, the heat generated would be so high that it could not be contained, and the reactor would melt down.
Control rods can attract neutrons and avoid interacting with uranium fuel. It is also a mechanism to regulate the number of nuclear reactions depending on the electricity demand.
The containment building is where the nuclear reactor and the primary circuit are located. The containment building is designed to contain possible explosions and prevent the potential escape of atomic radiation to the outside.
How is electricity generated?
When the steam has driven the turbine, it has transferred much of its thermal energy to the turbine. Then, finally, the steam turbine is connected to an electrical generator to transform the circular motion into electrical power.

The steam leaving the turbine has lost a lot of heat energy; however, it is still its temperature is still very high.
On leaving the turbine, the steam is directed to a condensation tank where it is in thermal contact with cold water pipes from the outside. When the water vapor becomes liquid, it returns to the reactor driven by a water pump.
